Difference between revisions of "Chapter Eight: Treatment of Waters With Special Contaminants"
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | = | + | = Chapter 8: TREATMENT OF WATERS WITH SPECIAL CONTAMINANTS = |
| − | + | <div style="text-align: justify"> | |
In recent times, there has been an emergence of water contaminants which in | In recent times, there has been an emergence of water contaminants which in | ||
the past, were either of less concern or their health impacts not known. These | the past, were either of less concern or their health impacts not known. These | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
methods for these special contaminants have also been presented. | methods for these special contaminants have also been presented. | ||
| − | == | + | ==NATURAL ORGANIC MATTER == |
Over the past 10–20 years, the amount of natural organic matter (NOM) has | Over the past 10–20 years, the amount of natural organic matter (NOM) has | ||
increased in raw water supplies in several areas. The presence of NOM causes | increased in raw water supplies in several areas. The presence of NOM causes | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
and (biological) filtration. | and (biological) filtration. | ||
| − | == | + | == ARSENIC == |
The occurrence of arsenic in groundwater is increasingly becoming a serious | The occurrence of arsenic in groundwater is increasingly becoming a serious | ||
pollution problem to human health worldwide. The occurrence of such pollutants | pollution problem to human health worldwide. The occurrence of such pollutants | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
techniques11. | techniques11. | ||
| − | == | + | == RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINANTS== |
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological contamination, is the | Radioactive contamination, also called radiological contamination, is the | ||
deposition or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, | deposition or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
Water sources with radioactive contamination should not be exploited by any | Water sources with radioactive contamination should not be exploited by any | ||
water authority or project. | water authority or project. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == FLUORIDE == | ||
| + | In Tanzania, fluorides are distributed in the regions of Arusha, Moshi, Singida, and | ||
| + | Shinyanga, with a severely affected area being on the foothills of Mount Meru and | ||
| + | Kilimanjaro. De-fluoridation of water is necessary when fluoride concentration is | ||
| + | higher than the acceptable limits as per Tanzania Standards. Excessive fluorides | ||
| + | in drinking water may cause mottling of teeth or dental fluorosis, a condition | ||
| + | resulting in the coloration of the tooth enamel, with chipping of the teeth in | ||
| + | severe cases, particularly in children. With even higher levels of fluorides, there | ||
| + | are cases of fluorosis of the bony structure. The chief sources of fluorides in | ||
| + | nature are fluorapatite (phosphate rock), fluorspar, crylite and igneous rocks | ||
| + | containing fluorosilicates. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In deciding whether or not to include de-fluoridation in a water supply scheme, the | ||
| + | designer should consider both the number of potential consumers, alternative | ||
| + | sources of water, financial consequences both capital and running costs of the | ||
| + | de-fluoridation plant and whether or not there is a possibility to dilute the water | ||
| + | containing fluoride in the effort to reduce fluoride concentration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == TOXIC CYANOBACTERIA IN DRINKING WATER == | ||
| + | Concern about the effects of cyanobacteria on human health has also grown | ||
| + | in many countries in recent years for a variety of reasons. These include cases | ||
| + | of poisoning attributed to toxic cyanobacteria and awareness of contamination | ||
| + | of water sources (especially lakes) resulting in increased cyanobacterial growth. | ||
| + | Cyanobacteria also continue to attract attention in part because of well-publicised | ||
| + | incidents of animal poisoning. The problems associated with cyanobacteria | ||
| + | are likely to increase in areas experiencing population growth with a lack of | ||
| + | concomitant sewage treatment and in regions with agricultural practices causing | ||
| + | nutrient losses to water bodies through over-fertilization and erosion. This | ||
| + | problem shall also increase in areas depending on dams for water provision | ||
| + | especially where the dams are shared with livestock. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Outbreaks of human poisoning attributed to toxic cyanobacteria have been | ||
| + | reported in Australia, following the exposure of individuals to contaminated | ||
| + | drinking water, and in the UK, where army recruits were exposed to the danger | ||
| + | through swimming and/or canoeing. However, the only known human fatalities | ||
| + | associated with cyanobacteria and their toxins occurred in Caruaru, Brazil, where | ||
| + | exposure through renal dialysis led to the death of over 50 patients. Fortunately, | ||
| + | such severe effects on human health appear to be rare, but little is known of the | ||
| + | scale and nature of either long-term effects (such as growth of tumours and liver | ||
| + | damage) or milder short-term effects, such as contact irritation. Eutrophication | ||
| + | is the main contributor to the occurrence of cyanobacteria. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Tanzania, eutrophication is one of the most common water quality pollution | ||
| + | challenges facing Lake Victoria today. Despite numerous and intensive research | ||
| + | efforts to alleviate the problem, the present extent and magnitude of the problem | ||
| + | is unprecedented (Myanza et al., 2014).High phycocyanin (PC) pigment values | ||
| + | (19.9 to 495 μg/l) unique to cyanobacteria have also been reported. The PC values | ||
| + | are well above the WHO alert level of 30 μg/l in earthen dams in Arusha (Eliakimu, | ||
| + | Machunda et al. 2018) and is associated with a variety of toxins affecting humans | ||
| + | and animals. These dams are shared between animals (wild and domesticated) | ||
| + | and humans. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Human influences such as population growth, urbanization and agriculture | ||
| + | contribute to the cause of algal blooms which disrupt natural food webs. | ||
| + | Furthermore, some algae are toxic e.g. blue-green algae, also known as | ||
| + | cyanobacteria. Algae are responsible for water odours and tastes, as well as | ||
| + | toxins, though attempts to use odour and taste as potential surrogates for the | ||
| + | presence of toxins are inconclusive. Because of concern about the potential | ||
| + | detrimental water quality impacts on human and animal health, eutrophication | ||
| + | necessitates active water source control and monitoring of water quality. | ||
| + | Eutrophic water increases the costs of water treatment and water supply to | ||
| + | consumers. Climate change amplifies eutrophication as rising temperatures | ||
| + | favour cyanobacteria over other phytoplankton species (e.g. diatoms). Warming | ||
| + | of surface waters also enhances vertical stratification of lakes, again favouring | ||
| + | the growth of cyanobacteria. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Eutrophication is the enhancement of the natural process of biological production | ||
| + | in rivers, lakes and reservoirs, caused by increases in levels of nutrients, usually | ||
| + | through phosphorus and nitrogen compounds. Eutrophication can result in | ||
| + | visible cyanobacterial or algal blooms, surface scums, floating plant mats and | ||
| + | benthic macrophyte aggregations. The decay of this organic matter may lead to | ||
| + | the depletion of dissolved oxygen in the water, which in turn can cause secondary | ||
| + | problems such as fish mortality from lack of oxygen and liberation of toxic | ||
| + | substances or phosphates that were previously bound to oxidized sediments. | ||
| + | Phosphates released from sediments accelerate eutrophication, thus closing a | ||
| + | positive feedback cycle. Some lakes are naturally eutrophic but, in many the excess | ||
| + | nutrient input is of anthropogenic origin, resulting from municipal wastewater | ||
| + | discharges or run-off from fertilizers and manure spread on agricultural areas. | ||
| + | Losses of nutrients due to erosion and run-off from soils may be low in relation | ||
| + | to agricultural input and yet high in relation to the eutrophication they cause, | ||
| + | since even low concentrations of phosphorus of less than 0.1 mgl-1 are sufficient | ||
| + | to induce a cyanobacterial bloom. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Design considerations and procedures for cyanobacterial removal from water sources'''<br> | ||
| + | It is important to consider the removal of cyanobacteria when designing a water | ||
| + | treatment plant. The design consideration for cyanobacterial removal should be | ||
| + | centred more in lakes and water reservoirs. The areas of concern should be those | ||
| + | which will be using Lake Victoria, various types of dams where water is likely to | ||
| + | be polluted by organic matter and nutrients and reservoirs as their source of | ||
| + | water supply. A combination of water treatment units and modules as presented | ||
| + | in the preceding section is recommended for the effective and efficiency toxic | ||
| + | cyanobacterial removal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For dams, provision should be included in the design to limit intrusion of animals | ||
| + | into the water for domestic purposes by providing cattle troughs where animals | ||
| + | can access drinking water without polluting other areas of the resource. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == AVAILABLE METHODS FOR THE REMOVAL OF SPECIAL WATER CONTAMINANTS == | ||
| + | The following methods may be considered for attaining ensuring that water is | ||
| + | free from contaminants.<br> | ||
| + | * Desalination | ||
| + | * Additive methods | ||
| + | * Adsorption methods | ||
| + | * Reverse Osmosis | ||
| + | * Membrane filtration | ||
| + | * Capacitive De-Ionization (CDI) | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Desalination=== | ||
| + | Desalination effectively removes all dissolved impurities from water. This can | ||
| + | be accomplished in one of several ways, such as by freezing, by distillation, by | ||
| + | electrolysis, Capacitive Deionization (CDI) or by reverse osmosis (RO). There are | ||
| + | some research efforts to use biomass12 based materials for de-fluoridation. The | ||
| + | cost of desalination is high although the costs of reverse osmosis have fallen | ||
| + | considerably in recent years. Nevertheless, this method is more appropriate | ||
| + | in dealing with brackish or sea water although it should not be entirely ruled | ||
| + | out where there a few, if any, alternative sources and there is a good supply of | ||
| + | electricity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Additive Method === | ||
| + | In this method, one or more chemicals are added to water. The fluoride is then | ||
| + | absorbed and both the additive and the fluoride are consequently removed by | ||
| + | using conventional treatment processes such as sedimentation and filtration. | ||
| + | A wide variety of materials have been tried for the purpose including lime, | ||
| + | magnesium sulphate, magnesium oxide, calcium phosphate, aluminium sulphate, | ||
| + | various natural earths, bauxite, sodium silicate and sodium aluminate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Excessive lime treatment for softening affect removal of fluoride is used due | ||
| + | to its absorption by the magnesium hydroxide floc. However, sizeable fluoride | ||
| + | removal is possible only when magnesium is present in large quantities which | ||
| + | may not always be the case, and magnesium may have to be supplemented in | ||
| + | the form of salts. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The initial cost and actual cost of chemicals is very high and the resultant sludge | ||
| + | is environmentally difficult to dispose of. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Adsorption Methods === | ||
| + | Adsorption methods employ a bed or filter of generally insoluble material | ||
| + | through which the water is allowed to percolate periodically. As the filter becomes | ||
| + | saturated with the fluoride ‘removed, the absorptive media is either replaced or | ||
| + | appropriately regenerated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The materials used have included charred bone, activated alumina, activated | ||
| + | carbon, tri-calcium phosphate, natural and synthetic ion exchange materials | ||
| + | and aluminium sulphate. Studies elsewhere have revealed that activated carbon | ||
| + | has a good capacity to remove fluoride where the concentration is less than 10 | ||
| + | mg/l. and the water is low in salinity. An activated carbon for fluoride removal | ||
| + | has been developed in India by carbonising paddy husk or saw dust, digesting | ||
| + | under pressure with alkali and quenching it in a 2% alum solution. The spent | ||
| + | material can be regenerated by soaking it in a 2% alum solution. Also a granular | ||
| + | ion exchange material, ‘Defluoron 2’, which is coal operating on the aluminium | ||
| + | cycle has been developed in India. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The bone char method developed and promoted by the Ngurdo to De-fluoridation | ||
| + | Research Station (NDRS) of the MOW has been widely applied for domestic and | ||
| + | institutional point of de-fluoridation. In recent times Reverse Osmosis (RO) has | ||
| + | been applied for desalination at Gairo small town, in Morogoro and in Arusha for | ||
| + | de-fluoridation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Capacitive Deionization (CDI) === | ||
| + | Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a technology to de-ionize water by applying an | ||
| + | electrical potential difference over two electrodes, which are often made of | ||
| + | porous carbon. Anions, that is ions with a negative charge, are removed from | ||
| + | the water and are stored in the positively polarized electrode. Likewise, cations | ||
| + | (positive charge) are stored in the cathode, which is the negatively polarized | ||
| + | electrode. Today, CDI is mainly used to remove ion materials such as Fluoride, | ||
| + | Nitrate, Lime, and salinity water. Other technologies for the deionization of | ||
| + | water are distillation, reverse osmosis and electro-dialysis. Compared to reverse | ||
| + | osmosis and distillation, CDI is an energy-efficient technology for removal of ions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A Korean company has produced CDI which remove fluoride and dissolved | ||
| + | salinity in water without chemicals or clogging membranes. This technology is | ||
| + | called MCDI and it removes ionized materials in water by using state of the art | ||
| + | electrodes running with very small amount of electricity of just 1.5 volts. (Figure | ||
| + | 8.1) Its operational cost is lower than any other known de-fluoridation and | ||
| + | desalination technologies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Figure8.1.JPG|649px|link=Chapter_Eight:_Treatment_of_Waters_With_Special_Contaminants]] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Membrane Filtration === | ||
| + | Membrane filtration is a process of physical separation of solid particles that uses | ||
| + | a semi-permeable membrane to remove suspended solids from a liquid stream. | ||
| + | Microfiltration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nanofiltration (NF) and Reverse Osmosis | ||
| + | (RO) are all examples of various pressure-driven membrane filtration techniques | ||
| + | that are used in the treatment of drinking water and sometimes in recovery of | ||
| + | wastewater. Membrane filters are semi-permeable materials that allow various | ||
| + | particle sizes to either flow through or to be trapped. These filters can remove | ||
| + | fine particles that are smaller than 2 μm as opposed to porous media filters | ||
| + | that can remove particles that range from 1 – 2 μm (SAMCO, 2020). Membrane | ||
| + | Filters can remove certain ions and particles from water. In this section, further | ||
| + | discussions will concentrate on NF, UF and MF. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nano-filtration (NF) is one of the most important recent developments in drinking | ||
| + | water treatment as well as in process industries. NF shows performance | ||
| + | characteristics that fall somewhere in between that of UF and RO membranes | ||
| + | (Agboola et al, 2014). NF is capable of removing finer contaminants than MF and UF. | ||
| + | In comparison to RO, NF entails slightly coarser filtration than RO and can remove | ||
| + | particles as small as 0.002 – 0.005 μm diameter including pesticide components | ||
| + | and organic micro-molecular particles. NF can remove larger divalent ions like | ||
| + | calcium sulphate but it allows sodium chloride to pass through. They can remove | ||
| + | contaminants based on their particle size as well as their electrical charge. NF | ||
| + | can remove the following: bacteria, calcium, colloidal particles, fluoride, iron, | ||
| + | manganese, organic materials, salt, viruses, hardness, heavy metals, nitrates, | ||
| + | sulphates and total dissolved solids. In water and wastewater treatment, NF is | ||
| + | applied to produce potable drinking water, to soften water, to remove nitrates, | ||
| + | to remove pesticides from surface or groundwater and to demineralise valuable | ||
| + | by-products like metals from wastewater. The design of the NF is based on the | ||
| + | flux which is the volume of water passing through a membrane in a given time | ||
| + | (litres/cm2). The designs are given by the manufacturers but are dependent on | ||
| + | the water quality, temperature and the salinity. Another design parameter is the | ||
| + | flow rate as given by the manufacturers in (litres per minute/cm2) [10-14 GPM/ | ||
| + | ft2]. NF are recommended for filtration of highland streams of fresh groundwater | ||
| + | that may be hard. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Microfiltration (MF) and Ultrafiltration (UF) are membrane filtration techniques | ||
| + | that are, in principal, similar to NF but have pore sizes that are bigger than NF | ||
| + | and these are 0.1 - 10μm and 0.1 – 0.01μ, respectively. Hence, MF membranes | ||
| + | have larger pore sizes and allow monovalent and multivalent ions and viruses | ||
| + | through but block certain bacteria and suspended solids. MF/UF can remove | ||
| + | particulates, bacteria, viruses, organic materials, certain dyes, colour, improves | ||
| + | taste and odour. They are both used as pre-treatments for NF and RO in order | ||
| + | to reduce the chances of RO fouling. In treatment plants that use porous media | ||
| + | filters, these membrane filters should be located downstream of such filters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following are common features of the three membrane filters:<br> | ||
| + | * The membrane filters are made as Hollow fibres, Plate and frame, Spiralwound or Tubular shaped. | ||
| + | * The pertinent components include; a cartridge filter, membrane module, pressure pump, water supply, clean in place system (CIP) and a holding tank. | ||
| + | * Membranes are manufactured as composite from; cellulose acetate, polyamides, polysulfone, polyethylene terephthalate, Aluminium. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Figure8.2.JPG|653px|link=Chapter_Eight:_Treatment_of_Waters_With_Special_Contaminants]] <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Reverse Osmosis === | ||
| + | Reverse osmosis is the process of forcing a solvent from a region of high solute | ||
| + | concentration through a membrane to a region of low solute concentration by | ||
| + | applying a pressure in excess of the osmotic pressure. It is a technology that is | ||
| + | used to remove the majority of contaminants from water by pushing the water | ||
| + | under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane. It occurs when the water | ||
| + | is moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient, i.e. from | ||
| + | lower concentration to higher concentration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Detail Features of RO'''<br> | ||
| + | * The RO semi-permeable membrane has pores large enough to admit water molecules; Hardness ions such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ remain behind and are flushed away by excess water into a drain. The process involves the reversal of flow through a membrane from a high salinity, or concentrated, solution to the high purity, or permeate, stream on the opposite side of the membrane. | ||
| + | * RO takes advantage of hydrostatic pressure gradients across the membrane. Pressure is used as the driving force for the separation. The applied pressure must be in excess of the osmotic pressure of the dissolved contaminants to allow the flow across the membrane. For example, the membrane may allow the passage of water molecules, but blocks molecules of dissolved salt. | ||
| + | * The membrane retains unwanted molecules while the ultra-pure water continues on for use or further treatment. This process takes any unwanted molecules retained by the membrane and sweeps them away to the drain. | ||
| + | * The resulting soft water supply is free of hardness ions without any other ions being added. Membranes have a limited capacity, therefore, require regular replacement as recommended by their manufacturers | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Impurities that are removed by RO'''<br> | ||
| + | * Heavy metals in the water | ||
| + | * Minerals/saline | ||
| + | * Fluoride | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Desalination of Water by Reverse Osmosis'''<br> | ||
| + | Desalination effectively removes all dissolved impurities from water. This can | ||
| + | be accomplished in one of several ways, including by freezing, by distillation, by | ||
| + | electrolysis or by reverse osmosis. The cost of desalination is high although the | ||
| + | costs of reverse osmosis have fallen considerably in recent years. Nevertheless, | ||
| + | this method is more appropriate in dealing with brackish or sea water although | ||
| + | it should not be entirely ruled out where there a few, if any, alternative sources | ||
| + | and there is a good supply of electricity. Therefore, of the several techniques | ||
| + | available for desalination and in the absence of large quantities of low grade | ||
| + | heat from power stations, the most promising method of desalination of both | ||
| + | brackish and sea water remains reverse osmosis (RO) whether it be for brackish | ||
| + | water or seawater. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reverse osmosis is the reverse of the normal osmosis process, which is the | ||
| + | natural movement of solvent from an area of low solute concentration, through a | ||
| + | membrane, to an area of high solute concentration when no external pressure is | ||
| + | applied. The membrane here is semi-permeable, meaning it allows the passage | ||
| + | of the solvent but not of solute. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Membranes used for reverse osmosis have a dense polymer barrier layer in | ||
| + | which separation takes place. In most cases the membrane is designed to allow | ||
| + | only water to pass through this dense layer while preventing the passage of the | ||
| + | solute (e.g. salt). This process requires that a high pressure be exerted on the | ||
| + | high concentration side of the membrane, usually 2-14 bar for fresh and brackish | ||
| + | water, and 40-70 bar for seawater, which has around a 24 bar natural osmotic | ||
| + | pressure which must be overcome. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Features of RO plants'''<br> | ||
| + | * Package plants are available from small single membrane units producing 20 l/hr of potable water to large units producing 20m3/hr and greater providing there is a good and reliable electricity supply; | ||
| + | * a competent workforce; and | ||
| + | * a potential area where these can prove competitive in coastal areas to deal with seasonal peaks such as occurs in tourist beach areas and where the alternative is the duplication of pipelines just to meet those peak demands as water can be readily blended with water from a surface source. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A diagram of the Reverse Osmosis process can be found at: ''https://softeningwater. | ||
| + | com/4-best-methods-of-water-softening/'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The Process of Reverse Osmosis'''<br> | ||
| + | Reverse Osmosis systems typically include a number of stages (Figure 8.2), | ||
| + | including:<br> | ||
| + | * a chlorine disinfectant stage; | ||
| + | * a sediment filter to trap particles including rust and calcium carbonate; | ||
| + | * a second filter stage often using sand/anthracite pressure filters; | ||
| + | * an activated carbon filter to trap organic chemicals and residual chlorine; | ||
| + | * One or two stages of high pressure pumps with an energy recovery turbine after the first stage; | ||
| + | * One or two stages of reverse osmosis (RO) filter with thin-film composite membranes; | ||
| + | * optionally a second carbon filter to capture those chemicals not removed by the RO membrane; and | ||
| + | * Disinfection of the remaining microbes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''REFERENCES'''<br> | ||
| + | Hezron T. Mwakabona, Mateso Said, Revocatus L. Machunda and Karoli N. Njau, (2015).<br> | ||
| + | Plant biomasses for de-fluoridation appropriateness: Unlocking their potentials.<br> | ||
| + | Research Journal in Engineering and Applied Sciences 3(3) 167-174.<br> | ||
| + | https://www.google.com/urlsa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.wikiwand.com%2Fen%2FCapacitive_deionization&psig | ||
| + | |||
| + | Previous Page: [[Chapter_Seven:_Water_Treatment|Chapter_Seven:_Water_Treatment]] << >> Next Page: [[Chapter_Nine:_Design_of_Water_Structures|Chapter_Nine:_Design_of_Water_Structures]] | ||
| + | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 11:03, 17 July 2022
Contents
1 Chapter 8: TREATMENT OF WATERS WITH SPECIAL CONTAMINANTS
In recent times, there has been an emergence of water contaminants which in the past, were either of less concern or their health impacts not known. These special contaminants are bringing new dimension in the manners in which they are supposed to be dealt with. This chapter presents special water contaminants that have emerged to be of major health concern. Treatment techniques and methods for these special contaminants have also been presented.
1.1 NATURAL ORGANIC MATTER
Over the past 10–20 years, the amount of natural organic matter (NOM) has increased in raw water supplies in several areas. The presence of NOM causes many problems in drinking water treatment processes, including: (i) having a negative effect on water quality by colour, taste and odour, (ii) increased requirement of coagulant and disinfectant dose, (which in turn results into increased sludge and potential harmful disinfection by-product formation), (iii) increased biological growth in the water distribution system, and (iv) increased levels of complex heavy metals and adsorbed organic pollutants.
In Tanzania, this problem of organic matter in water is more pronounced at the Igombe dam, the source of water supply for Tabora Municipality. A study on water quality monitoring at the Dam conducted between October 2009 – November 2010, revealed that colour and turbidity of raw water is very high due its very high humic content and algal blooms. These substances are mainly the result of organic matter from the surrounding dry forest.
From the conclusions of the first report (February 2, 2010), it is now known that the current treatment of water in the area is not sufficient to guarantee a good water quality in the network, mainly due to the risk of bacterial re-growth and also due to acidic pH, causing pipe corrosion. Igombe Dam water is characterized by high concentrations of organic matter. The organic matter is mainly of natural origin, that is, natural organic matter (NOM). The collected water quality data confirms the high amount of natural organic matter (NOM) in the raw water of the Igombe Dam.
The high concentration of NOM in this water may cause different problems, including excessive chlorine demand, formation of disinfection by-products (DBPs), bad taste and odour problems and bacterial re-growth in the distribution system. The low concentration of the different nitrogen compounds (nitrate, ammonia) in the raw water of the Igombe Dam indicates moderate to little agricultural and human activities in the watershed, confirming that the source of the organic matter in the raw water is principally of natural origin.
Therefore, one of the principal objectives of the future water treatment plant at Igombe will involve the reduction of NOM (measured as DOC and UV254) through different treatment processes - principally coagulation/sedimentation and (biological) filtration.
1.2 ARSENIC
The occurrence of arsenic in groundwater is increasingly becoming a serious pollution problem to human health worldwide. The occurrence of such pollutants can either be geogenic or anthropogenic. Recently, elevated concentrations of arsenic (>10 μg/L) has been reported in the northern parts of Tanzania and are associated with gold mining activities within or near the Lake Victoria Basin (LVB). The geology of LVB is dominated by greenstone belts in the North-Western region up to Mpanda and Lupa Mineral fields in the Ubendian system of western Tanzania. These regions are characterized by small, medium and large scale mining, using various technologies. Several adverse human health effects are noticed among the communities living around the relevant mining areas. Based on the developed geostatistical model using past study results on total arsenic in 9 districts, a spatial trend (R² =0.19) in the east-west transect was also noticed. In addition, a spatial trend (R² =0.009) was observed along the north-south transect. The reported study results are a potential to watch in engaging in improved drinking water supplies targeting groundwater sources.
Thus, every water treatment must consider removing this pollutant. One way of completely removing this pollutant is to consider a number of different units and modules such as to include oxidation, coagulation, flocculation, and membrane techniques11.
1.3 RADIOACTIVE CONTAMINANTS
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological contamination, is the deposition or presence of radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids or gases, where their presence is unintended or undesirable. Such contamination presents a health hazard because of the radioactive decay of the contaminants, which produces such harmful effects as ionizing radiation (namely α, β, and γ rays) and free neutrons. The sources of radioactive pollution can be classified into two groups: natural and man-made. In Tanzania such radioactive materials have been reported in geographical areas of Chemba and Bahi.
Water sources with radioactive contamination should not be exploited by any water authority or project.
1.4 FLUORIDE
In Tanzania, fluorides are distributed in the regions of Arusha, Moshi, Singida, and Shinyanga, with a severely affected area being on the foothills of Mount Meru and Kilimanjaro. De-fluoridation of water is necessary when fluoride concentration is higher than the acceptable limits as per Tanzania Standards. Excessive fluorides in drinking water may cause mottling of teeth or dental fluorosis, a condition resulting in the coloration of the tooth enamel, with chipping of the teeth in severe cases, particularly in children. With even higher levels of fluorides, there are cases of fluorosis of the bony structure. The chief sources of fluorides in nature are fluorapatite (phosphate rock), fluorspar, crylite and igneous rocks containing fluorosilicates.
In deciding whether or not to include de-fluoridation in a water supply scheme, the designer should consider both the number of potential consumers, alternative sources of water, financial consequences both capital and running costs of the de-fluoridation plant and whether or not there is a possibility to dilute the water containing fluoride in the effort to reduce fluoride concentration.
1.5 TOXIC CYANOBACTERIA IN DRINKING WATER
Concern about the effects of cyanobacteria on human health has also grown in many countries in recent years for a variety of reasons. These include cases of poisoning attributed to toxic cyanobacteria and awareness of contamination of water sources (especially lakes) resulting in increased cyanobacterial growth. Cyanobacteria also continue to attract attention in part because of well-publicised incidents of animal poisoning. The problems associated with cyanobacteria are likely to increase in areas experiencing population growth with a lack of concomitant sewage treatment and in regions with agricultural practices causing nutrient losses to water bodies through over-fertilization and erosion. This problem shall also increase in areas depending on dams for water provision especially where the dams are shared with livestock.
Outbreaks of human poisoning attributed to toxic cyanobacteria have been reported in Australia, following the exposure of individuals to contaminated drinking water, and in the UK, where army recruits were exposed to the danger through swimming and/or canoeing. However, the only known human fatalities associated with cyanobacteria and their toxins occurred in Caruaru, Brazil, where exposure through renal dialysis led to the death of over 50 patients. Fortunately, such severe effects on human health appear to be rare, but little is known of the scale and nature of either long-term effects (such as growth of tumours and liver damage) or milder short-term effects, such as contact irritation. Eutrophication is the main contributor to the occurrence of cyanobacteria.
In Tanzania, eutrophication is one of the most common water quality pollution challenges facing Lake Victoria today. Despite numerous and intensive research efforts to alleviate the problem, the present extent and magnitude of the problem is unprecedented (Myanza et al., 2014).High phycocyanin (PC) pigment values (19.9 to 495 μg/l) unique to cyanobacteria have also been reported. The PC values are well above the WHO alert level of 30 μg/l in earthen dams in Arusha (Eliakimu, Machunda et al. 2018) and is associated with a variety of toxins affecting humans and animals. These dams are shared between animals (wild and domesticated) and humans.
Human influences such as population growth, urbanization and agriculture contribute to the cause of algal blooms which disrupt natural food webs. Furthermore, some algae are toxic e.g. blue-green algae, also known as cyanobacteria. Algae are responsible for water odours and tastes, as well as toxins, though attempts to use odour and taste as potential surrogates for the presence of toxins are inconclusive. Because of concern about the potential detrimental water quality impacts on human and animal health, eutrophication necessitates active water source control and monitoring of water quality. Eutrophic water increases the costs of water treatment and water supply to consumers. Climate change amplifies eutrophication as rising temperatures favour cyanobacteria over other phytoplankton species (e.g. diatoms). Warming of surface waters also enhances vertical stratification of lakes, again favouring the growth of cyanobacteria.
Eutrophication is the enhancement of the natural process of biological production in rivers, lakes and reservoirs, caused by increases in levels of nutrients, usually through phosphorus and nitrogen compounds. Eutrophication can result in visible cyanobacterial or algal blooms, surface scums, floating plant mats and benthic macrophyte aggregations. The decay of this organic matter may lead to the depletion of dissolved oxygen in the water, which in turn can cause secondary problems such as fish mortality from lack of oxygen and liberation of toxic substances or phosphates that were previously bound to oxidized sediments. Phosphates released from sediments accelerate eutrophication, thus closing a positive feedback cycle. Some lakes are naturally eutrophic but, in many the excess nutrient input is of anthropogenic origin, resulting from municipal wastewater discharges or run-off from fertilizers and manure spread on agricultural areas. Losses of nutrients due to erosion and run-off from soils may be low in relation to agricultural input and yet high in relation to the eutrophication they cause, since even low concentrations of phosphorus of less than 0.1 mgl-1 are sufficient to induce a cyanobacterial bloom.
Design considerations and procedures for cyanobacterial removal from water sources
It is important to consider the removal of cyanobacteria when designing a water
treatment plant. The design consideration for cyanobacterial removal should be
centred more in lakes and water reservoirs. The areas of concern should be those
which will be using Lake Victoria, various types of dams where water is likely to
be polluted by organic matter and nutrients and reservoirs as their source of
water supply. A combination of water treatment units and modules as presented
in the preceding section is recommended for the effective and efficiency toxic
cyanobacterial removal.
For dams, provision should be included in the design to limit intrusion of animals into the water for domestic purposes by providing cattle troughs where animals can access drinking water without polluting other areas of the resource.
1.6 AVAILABLE METHODS FOR THE REMOVAL OF SPECIAL WATER CONTAMINANTS
The following methods may be considered for attaining ensuring that water is
free from contaminants.
- Desalination
- Additive methods
- Adsorption methods
- Reverse Osmosis
- Membrane filtration
- Capacitive De-Ionization (CDI)
1.6.1 Desalination
Desalination effectively removes all dissolved impurities from water. This can be accomplished in one of several ways, such as by freezing, by distillation, by electrolysis, Capacitive Deionization (CDI) or by reverse osmosis (RO). There are some research efforts to use biomass12 based materials for de-fluoridation. The cost of desalination is high although the costs of reverse osmosis have fallen considerably in recent years. Nevertheless, this method is more appropriate in dealing with brackish or sea water although it should not be entirely ruled out where there a few, if any, alternative sources and there is a good supply of electricity.
1.6.2 Additive Method
In this method, one or more chemicals are added to water. The fluoride is then absorbed and both the additive and the fluoride are consequently removed by using conventional treatment processes such as sedimentation and filtration. A wide variety of materials have been tried for the purpose including lime, magnesium sulphate, magnesium oxide, calcium phosphate, aluminium sulphate, various natural earths, bauxite, sodium silicate and sodium aluminate.
Excessive lime treatment for softening affect removal of fluoride is used due to its absorption by the magnesium hydroxide floc. However, sizeable fluoride removal is possible only when magnesium is present in large quantities which may not always be the case, and magnesium may have to be supplemented in the form of salts.
The initial cost and actual cost of chemicals is very high and the resultant sludge is environmentally difficult to dispose of.
1.6.3 Adsorption Methods
Adsorption methods employ a bed or filter of generally insoluble material through which the water is allowed to percolate periodically. As the filter becomes saturated with the fluoride ‘removed, the absorptive media is either replaced or appropriately regenerated.
The materials used have included charred bone, activated alumina, activated carbon, tri-calcium phosphate, natural and synthetic ion exchange materials and aluminium sulphate. Studies elsewhere have revealed that activated carbon has a good capacity to remove fluoride where the concentration is less than 10 mg/l. and the water is low in salinity. An activated carbon for fluoride removal has been developed in India by carbonising paddy husk or saw dust, digesting under pressure with alkali and quenching it in a 2% alum solution. The spent material can be regenerated by soaking it in a 2% alum solution. Also a granular ion exchange material, ‘Defluoron 2’, which is coal operating on the aluminium cycle has been developed in India.
The bone char method developed and promoted by the Ngurdo to De-fluoridation Research Station (NDRS) of the MOW has been widely applied for domestic and institutional point of de-fluoridation. In recent times Reverse Osmosis (RO) has been applied for desalination at Gairo small town, in Morogoro and in Arusha for de-fluoridation.
1.6.4 Capacitive Deionization (CDI)
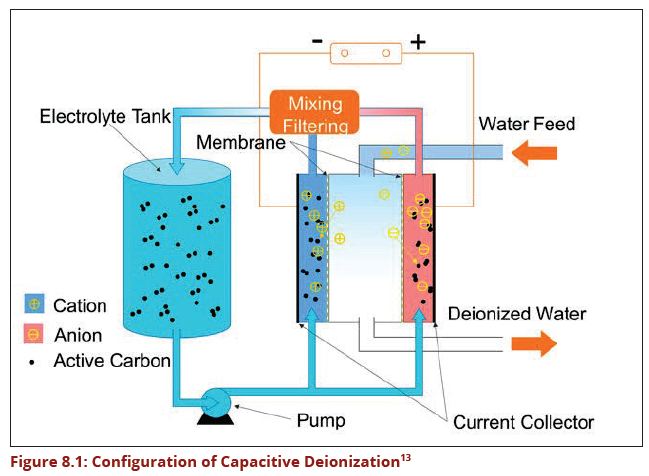
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a technology to de-ionize water by applying an electrical potential difference over two electrodes, which are often made of porous carbon. Anions, that is ions with a negative charge, are removed from the water and are stored in the positively polarized electrode. Likewise, cations (positive charge) are stored in the cathode, which is the negatively polarized electrode. Today, CDI is mainly used to remove ion materials such as Fluoride, Nitrate, Lime, and salinity water. Other technologies for the deionization of water are distillation, reverse osmosis and electro-dialysis. Compared to reverse osmosis and distillation, CDI is an energy-efficient technology for removal of ions.
A Korean company has produced CDI which remove fluoride and dissolved salinity in water without chemicals or clogging membranes. This technology is called MCDI and it removes ionized materials in water by using state of the art electrodes running with very small amount of electricity of just 1.5 volts. (Figure 8.1) Its operational cost is lower than any other known de-fluoridation and desalination technologies.
1.6.5 Membrane Filtration
Membrane filtration is a process of physical separation of solid particles that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove suspended solids from a liquid stream. Microfiltration (MF), Ultrafiltration (UF), Nanofiltration (NF) and Reverse Osmosis (RO) are all examples of various pressure-driven membrane filtration techniques that are used in the treatment of drinking water and sometimes in recovery of wastewater. Membrane filters are semi-permeable materials that allow various particle sizes to either flow through or to be trapped. These filters can remove fine particles that are smaller than 2 μm as opposed to porous media filters that can remove particles that range from 1 – 2 μm (SAMCO, 2020). Membrane Filters can remove certain ions and particles from water. In this section, further discussions will concentrate on NF, UF and MF.
Nano-filtration (NF) is one of the most important recent developments in drinking water treatment as well as in process industries. NF shows performance characteristics that fall somewhere in between that of UF and RO membranes (Agboola et al, 2014). NF is capable of removing finer contaminants than MF and UF. In comparison to RO, NF entails slightly coarser filtration than RO and can remove particles as small as 0.002 – 0.005 μm diameter including pesticide components and organic micro-molecular particles. NF can remove larger divalent ions like calcium sulphate but it allows sodium chloride to pass through. They can remove contaminants based on their particle size as well as their electrical charge. NF can remove the following: bacteria, calcium, colloidal particles, fluoride, iron, manganese, organic materials, salt, viruses, hardness, heavy metals, nitrates, sulphates and total dissolved solids. In water and wastewater treatment, NF is applied to produce potable drinking water, to soften water, to remove nitrates, to remove pesticides from surface or groundwater and to demineralise valuable by-products like metals from wastewater. The design of the NF is based on the flux which is the volume of water passing through a membrane in a given time (litres/cm2). The designs are given by the manufacturers but are dependent on the water quality, temperature and the salinity. Another design parameter is the flow rate as given by the manufacturers in (litres per minute/cm2) [10-14 GPM/ ft2]. NF are recommended for filtration of highland streams of fresh groundwater that may be hard.
Microfiltration (MF) and Ultrafiltration (UF) are membrane filtration techniques that are, in principal, similar to NF but have pore sizes that are bigger than NF and these are 0.1 - 10μm and 0.1 – 0.01μ, respectively. Hence, MF membranes have larger pore sizes and allow monovalent and multivalent ions and viruses through but block certain bacteria and suspended solids. MF/UF can remove particulates, bacteria, viruses, organic materials, certain dyes, colour, improves taste and odour. They are both used as pre-treatments for NF and RO in order to reduce the chances of RO fouling. In treatment plants that use porous media filters, these membrane filters should be located downstream of such filters.
The following are common features of the three membrane filters:
- The membrane filters are made as Hollow fibres, Plate and frame, Spiralwound or Tubular shaped.
- The pertinent components include; a cartridge filter, membrane module, pressure pump, water supply, clean in place system (CIP) and a holding tank.
- Membranes are manufactured as composite from; cellulose acetate, polyamides, polysulfone, polyethylene terephthalate, Aluminium.
1.6.6 Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is the process of forcing a solvent from a region of high solute concentration through a membrane to a region of low solute concentration by applying a pressure in excess of the osmotic pressure. It is a technology that is used to remove the majority of contaminants from water by pushing the water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane. It occurs when the water is moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient, i.e. from lower concentration to higher concentration.
Detail Features of RO
- The RO semi-permeable membrane has pores large enough to admit water molecules; Hardness ions such as Ca2+ and Mg2+ remain behind and are flushed away by excess water into a drain. The process involves the reversal of flow through a membrane from a high salinity, or concentrated, solution to the high purity, or permeate, stream on the opposite side of the membrane.
- RO takes advantage of hydrostatic pressure gradients across the membrane. Pressure is used as the driving force for the separation. The applied pressure must be in excess of the osmotic pressure of the dissolved contaminants to allow the flow across the membrane. For example, the membrane may allow the passage of water molecules, but blocks molecules of dissolved salt.
- The membrane retains unwanted molecules while the ultra-pure water continues on for use or further treatment. This process takes any unwanted molecules retained by the membrane and sweeps them away to the drain.
- The resulting soft water supply is free of hardness ions without any other ions being added. Membranes have a limited capacity, therefore, require regular replacement as recommended by their manufacturers
Impurities that are removed by RO
- Heavy metals in the water
- Minerals/saline
- Fluoride
Desalination of Water by Reverse Osmosis
Desalination effectively removes all dissolved impurities from water. This can
be accomplished in one of several ways, including by freezing, by distillation, by
electrolysis or by reverse osmosis. The cost of desalination is high although the
costs of reverse osmosis have fallen considerably in recent years. Nevertheless,
this method is more appropriate in dealing with brackish or sea water although
it should not be entirely ruled out where there a few, if any, alternative sources
and there is a good supply of electricity. Therefore, of the several techniques
available for desalination and in the absence of large quantities of low grade
heat from power stations, the most promising method of desalination of both
brackish and sea water remains reverse osmosis (RO) whether it be for brackish
water or seawater.
Reverse osmosis is the reverse of the normal osmosis process, which is the natural movement of solvent from an area of low solute concentration, through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration when no external pressure is applied. The membrane here is semi-permeable, meaning it allows the passage of the solvent but not of solute.
Membranes used for reverse osmosis have a dense polymer barrier layer in which separation takes place. In most cases the membrane is designed to allow only water to pass through this dense layer while preventing the passage of the solute (e.g. salt). This process requires that a high pressure be exerted on the high concentration side of the membrane, usually 2-14 bar for fresh and brackish water, and 40-70 bar for seawater, which has around a 24 bar natural osmotic pressure which must be overcome.
Features of RO plants
- Package plants are available from small single membrane units producing 20 l/hr of potable water to large units producing 20m3/hr and greater providing there is a good and reliable electricity supply;
- a competent workforce; and
- a potential area where these can prove competitive in coastal areas to deal with seasonal peaks such as occurs in tourist beach areas and where the alternative is the duplication of pipelines just to meet those peak demands as water can be readily blended with water from a surface source.
A diagram of the Reverse Osmosis process can be found at: https://softeningwater. com/4-best-methods-of-water-softening/
The Process of Reverse Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis systems typically include a number of stages (Figure 8.2),
including:
- a chlorine disinfectant stage;
- a sediment filter to trap particles including rust and calcium carbonate;
- a second filter stage often using sand/anthracite pressure filters;
- an activated carbon filter to trap organic chemicals and residual chlorine;
- One or two stages of high pressure pumps with an energy recovery turbine after the first stage;
- One or two stages of reverse osmosis (RO) filter with thin-film composite membranes;
- optionally a second carbon filter to capture those chemicals not removed by the RO membrane; and
- Disinfection of the remaining microbes.
REFERENCES
Hezron T. Mwakabona, Mateso Said, Revocatus L. Machunda and Karoli N. Njau, (2015).
Plant biomasses for de-fluoridation appropriateness: Unlocking their potentials.
Research Journal in Engineering and Applied Sciences 3(3) 167-174.
https://www.google.com/urlsa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.wikiwand.com%2Fen%2FCapacitive_deionization&psig
Previous Page: Chapter_Seven:_Water_Treatment << >> Next Page: Chapter_Nine:_Design_of_Water_Structures