Chapter Six: Pumping Systems
Contents
1 Chapter Six: Pumping Systems
1.1 Introduction
This section describes the water supply pumping systems. A brief presentation of types of pumps is provided. It describes how to design and select pumps for a water supply system. Lastly, it gives key considerations of their installation. It is important to understand the different types of pumps, design procedures, sources of pumping power, motor starting, machines protection and economics of electric power systems. More details on pump types and their functioning are given in Appendix E.
1.2 Rationale
The main goal of any water pumping plant and pumping system is to lift water from a lower to a higher level.
1.3 COMMON TYPES OF PUMPS USED IN WATER SUPPLY
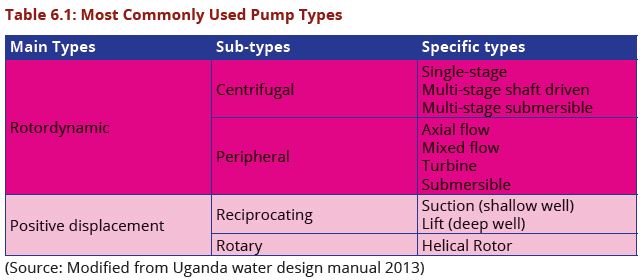
There are two main types of pumps used in water supply projects. The pumps are different in design and application. Table 6.1 shows the most commonly used pump types. Further details of each type of pump can be seen in Appendix E of this DCOM manual.
1.4 PUMPING SYSTEM SETUP
When setting up a pumping system, carefully calculate the driver Horsepower (HP) required based on the flow data, pressure and efficiency of the pump. Check the pump RPM and drive RPM and select the proper size pulleys to achieve the desired flow. Review the maximum horsepower per belt to assure that the pump receives adequate power to deliver the desired flow. The correct belt length and centre distance must be established to achieve the proper HP. If in doubt, consult your pump and/or drive supplier for their recommendations.
1.5 SOURCE OF PUMPING POWER
The different types of power sources commonly used for water supply pumps
include:
- Electrical grid power
- Diesel/gasoline generators and engines
- Natural gas/biogas generators
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
The choice of pumping energy depends on several factors namely:
- Availability of and proximity to grid power,
- Capital costs of the alternatives,
- Operational costs of the alternatives.
In Tanzania when deciding on water pumping energy, grid power is considered as the basic source in the sense that when available it becomes the 1st choice. It is only when the grid source is too far from the pumping point that other sources of power are considered. The three alternatives to grid power namely diesel/petrol/ natural gas/biogas generators or engines have both positives and negatives. In the following subchapter, each alternative shall be discussed.
1.6 PUMP SELECTION
Pump selection involves choosing the type of pump that fits the application and
sizing the pump to be able to deliver the required pressure and flow to the point
of delivery. The factors which should be considered in the selection and sizing of
a pump include:
- Depth to the water level and seasonal variations of the water source;
- Pressure ranges needed for adequate water supply;
- Heights through which water has to be lifted, both below and above the pump;
- Pump location; and
- Pump durability and efficiency.
The type of pump selected for a particular project should be determined on the basis of the following fundamental considerations:
- Yield of the well or water source;
- Daily needs and instantaneous demand of the users;
- The “usable water” in the pressure or storage tank;
- Size and alignment of the well casing;
- Total operating head pressure of the pump at normal delivery rates, including lift and all friction losses;
- Difference in elevation between ground level and water level in the well during pumping;
- Availability of power;
- Ease of maintenance and availability of replacement parts;
- First cost and economy of operation;
- Reliability of pumping equipment; and
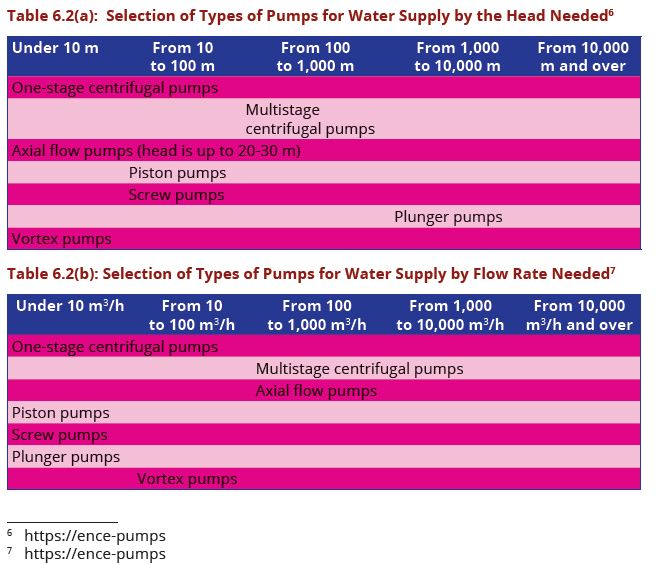
Tables 6.2(a) and (b) shows the operation ranges of different types of pumps according to the head required and the flow rate needed. For water supply pumps the two must be considered for a good pump. Examples of pump duty calculations are provided in Appendix E.
1.7 PUMP PROTECTION
In order to ensure acceptable technical soundness of plants and water pumping
systems the following protective measures need to be considered at the design
stage and adopted wherever desirable. For the purpose of avoiding unnecessary
sophistication and yet establish reliable protection of plants and pumping
systems the protective systems enumerated hereunder shall be adopted in the
fashion recommended herein:
1. Protection against dry running
2. Protection against water hammer
3. Protection against cavitation’s
4. Protection against overloads/over current
5. Protection against cathodic corrosion.
The most important protection is water hammer which can be analysed through number of software. Of these, the one recommended for consideration is Surge 2000 produced as part of the KY pipe software package, and its details can be found by logging on to their website. A 250 pipe solution costs US$ 3,000 in 2006.
Another alternative, especially if the designer is interested in is to pursue a controlled air transient technology (CATT) approach for the use of air-valves. This is available by contacting Vent-O-Mat of South Africa by logging on to their website.
REFERENCES
MoW 3rd Edition Design Manual, 2009
Uganda Water Design Manual, 2013
Previous Page: Chapter_Five:_Pipelines_Design << >> Next Page: Chapter_Seven:_Water_Treatment